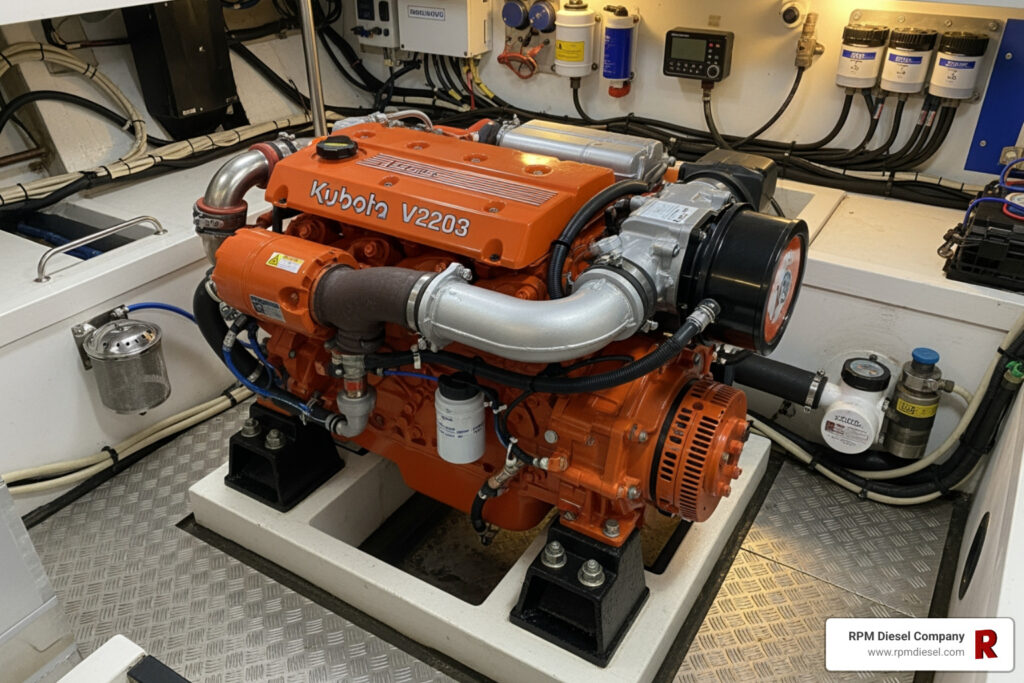
Why Kubota Diesel Engine Troubleshooting Matters for Marine Vessel Owners
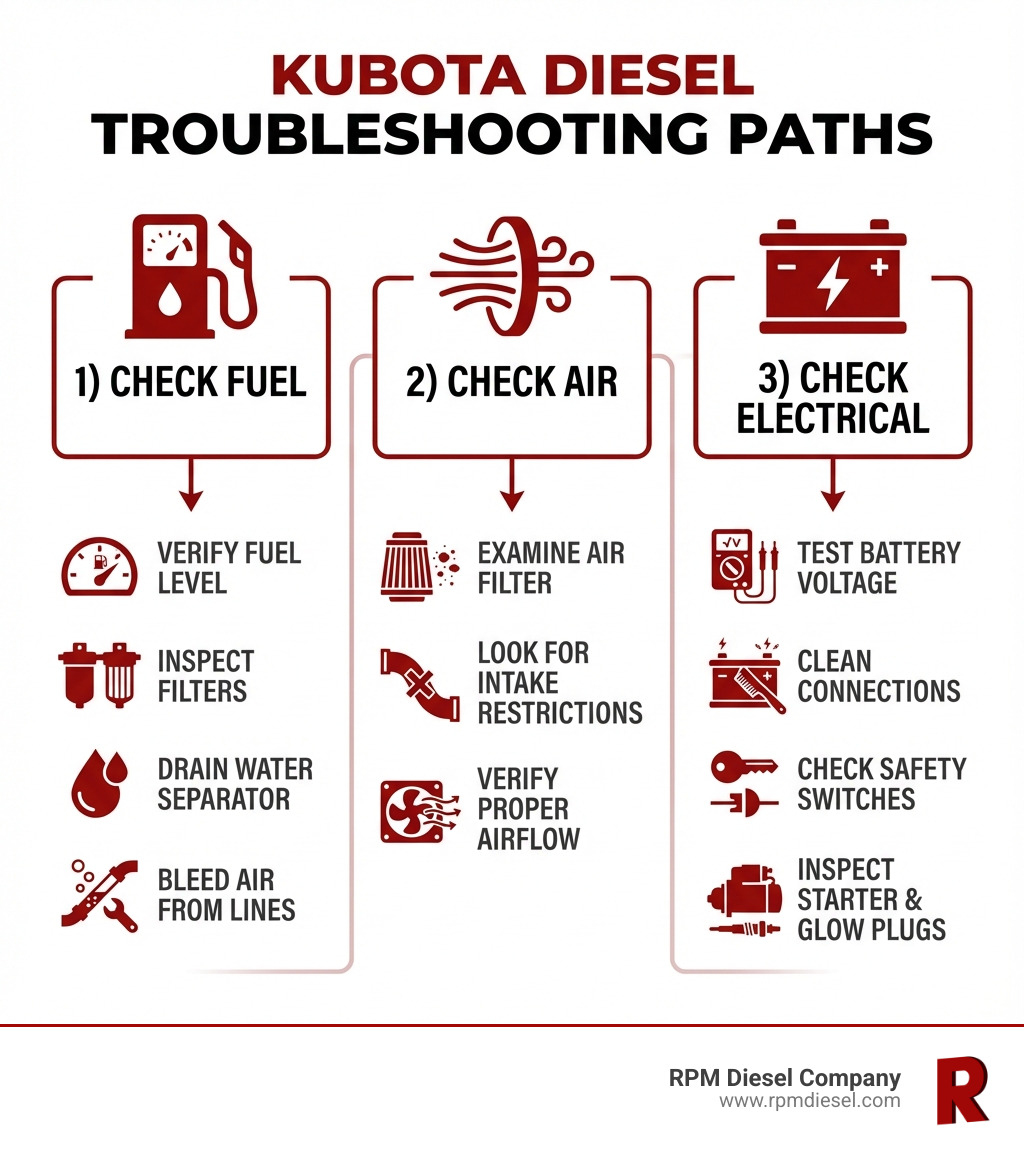
Kubota diesel engine troubleshooting is a critical skill for any marine vessel owner. When your engine won’t start or loses power miles offshore, knowing where to look first can mean the difference between a quick fix and an expensive tow. Here’s what you need to check immediately:
Quick Troubleshooting Checklist:
- Fuel System – Check fuel level, filters, and look for water contamination
- Electrical System – Test battery voltage (should be 12V or higher), check for corroded cables
- Air System – Inspect air filter for dirt or blockage
- Cooling System – Verify coolant level and check for overheating
- Safety Switches – Ensure all kill switches and interlocks are properly engaged
Kubota diesel engines are workhorses in marine vessels due to their reliability. However, the harsh marine environment—with its salt, moisture, and vibration—takes a toll. According to research, malfunctioning diesel engines are the most common cause for emergency rescue calls, particularly for fishing boats and charters.
The good news is that most Kubota diesel problems stem from minor issues like dirty battery cables, clogged fuel filters, or air in the fuel lines. These are often preventable with routine maintenance and straightforward to fix if you know what to look for.
This guide walks you through systematic troubleshooting for common Kubota marine diesel problems, from no-start conditions and power loss to interpreting exhaust smoke. Whether you’re dealing with a cranking engine that won’t fire or mysterious power loss under load, we’ll help you pinpoint the cause.
Safety first: Always disconnect the battery negative cable before working on electrical systems. Allow hot components to cool before touching them. Never open high-pressure fuel systems, and ensure adequate ventilation when running your engine.
Engine Won’t Start: Diagnosing the Core Problem
When your Kubota diesel engine refuses to start, a systematic approach is key. No-start conditions fall into two main types: the engine cranks but won’t start, or the engine doesn’t crank at all. The cause is almost always an issue with the electrical or fuel system.
Electrical System Checks
If your engine isn’t cranking, or cranks weakly, the electrical system is your first suspect. How can we troubleshoot electrical system issues in a Kubota diesel engine?
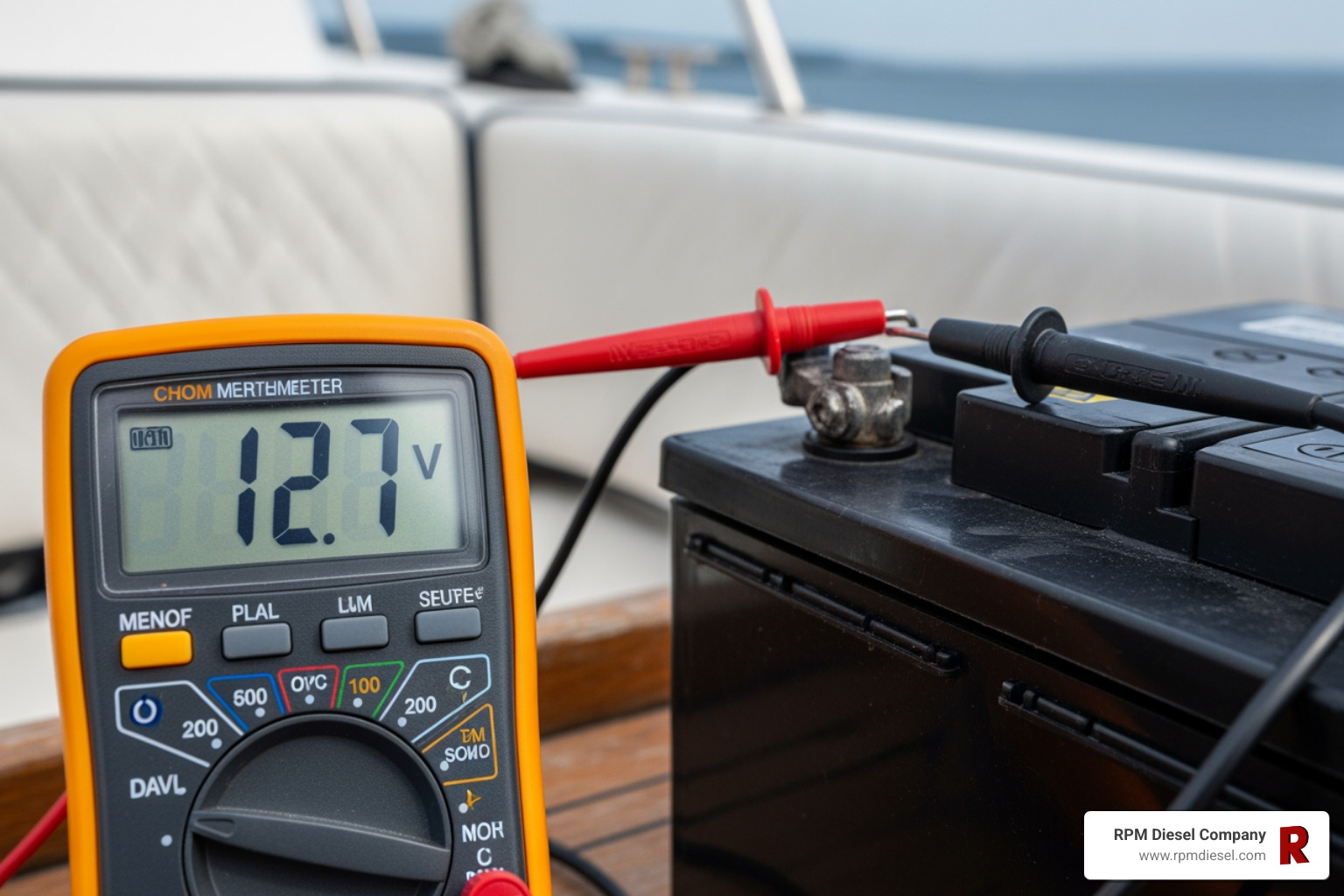
- Battery Testing: A weak or dead battery is a top suspect. Use a voltmeter; a healthy battery should read ~12.6V. Below 12V, it needs charging or replacement. The starter may engage above 11V, but it’s a sign of a weak battery.
- Battery Cables and Connections: Corroded or loose cables can block power even with a good battery. Clean posts and terminals, ensuring all connections are tight.
- Fuses and Fusible Links: A dead electrical system points to blown fuses or fusible links (often near the starter). These protect from overcurrent and commonly blow from reversed battery polarity.
- Safety Switches: Safety switches (e.g., neutral safety) prevent starting in unsafe conditions. If the battery is good but the engine won’t crank, test these switches for continuity.
- Starter Motor and Solenoid: With other electricals cleared, suspect the starter motor or solenoid. A clicking sound often points to a bad solenoid or low power to the starter.
- Glow Plugs: Glow plugs are essential for cold starts, preheating the combustion chamber. Faulty plugs can prevent the engine from firing, even if it cranks.

Fuel System Faults: The Most Common Culprit
If the engine cranks but won’t start, focus on the fuel system. Common fuel-related problems include:
- No Fuel or Low Fuel: Always check the fuel level visually; gauges can be faulty.
- Clogged Fuel Filters: Clogged primary and secondary fuel filters are a frequent cause of no-starts. Replace them regularly per your maintenance schedule.
- Contaminated Fuel:
- Degraded Diesel Fuel: Degraded fuel causes white smoke and hard starts. If suspected, drain the tank, replace filters, refill with fresh diesel, and bleed the system.
- Water in Fuel: Water in fuel is a severe marine problem, often indicated by white smoke. The fix is to drain and clean the tank, replace filters, and bleed the lines.
- Gasoline Contamination: What steps should we take if we suspect gasoline has contaminated our diesel fuel? This is a critical error that can destroy the injection system. Do not start the engine. The entire fuel system must be drained, flushed, and refilled with fresh diesel after replacing filters.
- Air in Fuel Lines: Air in the fuel lines, often from running out of fuel or changing filters, will prevent starting. The system must be bled.
- Clogged Fuel Pickup Screen: A clogged fuel pickup screen in the tank can restrict fuel flow. Access the tank to inspect it. The lift pump draws fuel from the tank; test it by checking for flow during manual priming or cranking.
- Injection Pump Issues: A stuck fuel control lever or faulty electric stop solenoid on the injection pump can halt fuel delivery. Check the solenoid’s operation and try penetrating oil on a stuck lever. For detailed diagrams, consult your engine’s shop manual. For a quick reference, see this helpful guide to Kubota shop manuals.
How to Bleed Air from a Kubota Fuel System
Air in the fuel system is a common reason a diesel engine cranks but won’t start. Here’s how we bleed air from a Kubota diesel fuel system:
Symptoms of Air in the Fuel System:
- Engine cranks but won’t start.
- Engine starts, runs briefly, then dies.
- Engine runs erratically or misfires.
Tools You Might Need:
- Wrenches
- Clean rags
- Container for spilled fuel
Steps to Bleed the Fuel System:
- Ensure Fuel Supply: Confirm you have ample fresh diesel fuel.
- Locate Bleeder Screws: Locate bleeder screws on the fuel filter housing and injection pump. Consult your service manual for specifics.
- Prime the System (if applicable): Use the hand primer pump, if equipped, until you feel resistance. This pushes fuel through the system.
- Bleed at the Fuel Filter:
- Loosen the bleeder screw on the fuel filter.
- Use the primer or crank the engine in short bursts (10-15 seconds max) until fuel flows without air bubbles.
- Tighten the screw.
- Bleed at the Injection Pump (if necessary): If it still won’t start, repeat the process at the injection pump’s bleeder screw.
- Bleed at the Injector Lines (if all else fails):
- As a last resort, carefully loosen the fuel line nut at an injector.
- Crank the engine until fuel squirts out, then tighten.
- Caution: High-pressure fuel is dangerous; keep clear.
- Attempt Start: Try starting the engine. It may take a few cranks to purge all air.
Mechanical No-Start Issues
While less common, mechanical issues can also prevent a start.
- Hydraulic Lock: What is a ‘hydraulic lock’ in an engine, and how do we fix it? A hydraulic lock is when fluid (usually water in a marine engine) fills a cylinder, preventing the piston from moving. Attempting to start it can cause severe damage.
- How to Fix a Hydraulic Lock: If you suspect a hydraulic lock, do not attempt to force the engine to turn.
- Remove the glow plugs or injectors.
- Carefully hand-turn the engine to push out any trapped fluid.
- Once the engine turns freely, replace the glow plugs/injectors.
- Change the engine oil and filter immediately, as it will be contaminated.
- Change the oil again after a few hours of operation to remove any remaining contaminants.
- How to Fix a Hydraulic Lock: If you suspect a hydraulic lock, do not attempt to force the engine to turn.
- Seized Engine: A seized engine won’t crank at all, even with a good battery. Caused by severe overheating or lack of oil, it requires a major overhaul.
- Compression Loss: Low compression from worn rings, bad valves, or a blown head gasket prevents combustion. This requires a professional diagnosis and repair.
- Timing Issues: Incorrect engine timing from a broken belt or gear will prevent the engine from starting. This is a complex repair for a professional.
Solving Performance Problems: A Guide to Kubota Diesel Engine Troubleshooting
Performance issues like losing power, running rough, or overheating can compromise your vessel’s reliability and safety.
Engine Losing Power or Bogging Down
An engine losing power or “bogging down” under load is a serious concern. What are the signs of an engine bogging down under load in a Kubota diesel engine? You’ll notice a drop in RPMs and a struggle to maintain speed.
What are the potential causes of a Kubota diesel engine losing power when it heats up? This often points to:
- Fuel Starvation:
- Clogged Fuel Filters: Partially clogged filters restrict fuel flow under load.
- Weak Lift Pump: A failing lift pump won’t supply enough fuel to the injection pump.
- Clogged Fuel Pickup Screen: Debris in the tank can block the fuel pickup.
- Air Leaks in Fuel Lines: Air entering the system causes inconsistent fuel delivery.
- Restricted Air Intake: A clogged air filter starves the engine of air, causing power loss.
- Exhaust Restriction: A blocked exhaust creates back pressure, reducing power.
- Overheating: An overheating engine loses power as a self-preservation measure.
- Injector Issues: Dirty or worn injectors cause poor fuel atomization and power loss.
- Injection Pump Wear: A worn injection pump may fail to deliver enough fuel under load.
Interpreting Exhaust Smoke: White, Blue, or Black
The color of your exhaust smoke is a key diagnostic tool. What are the common causes of white, blue, or black smoke from a Kubota diesel engine exhaust?
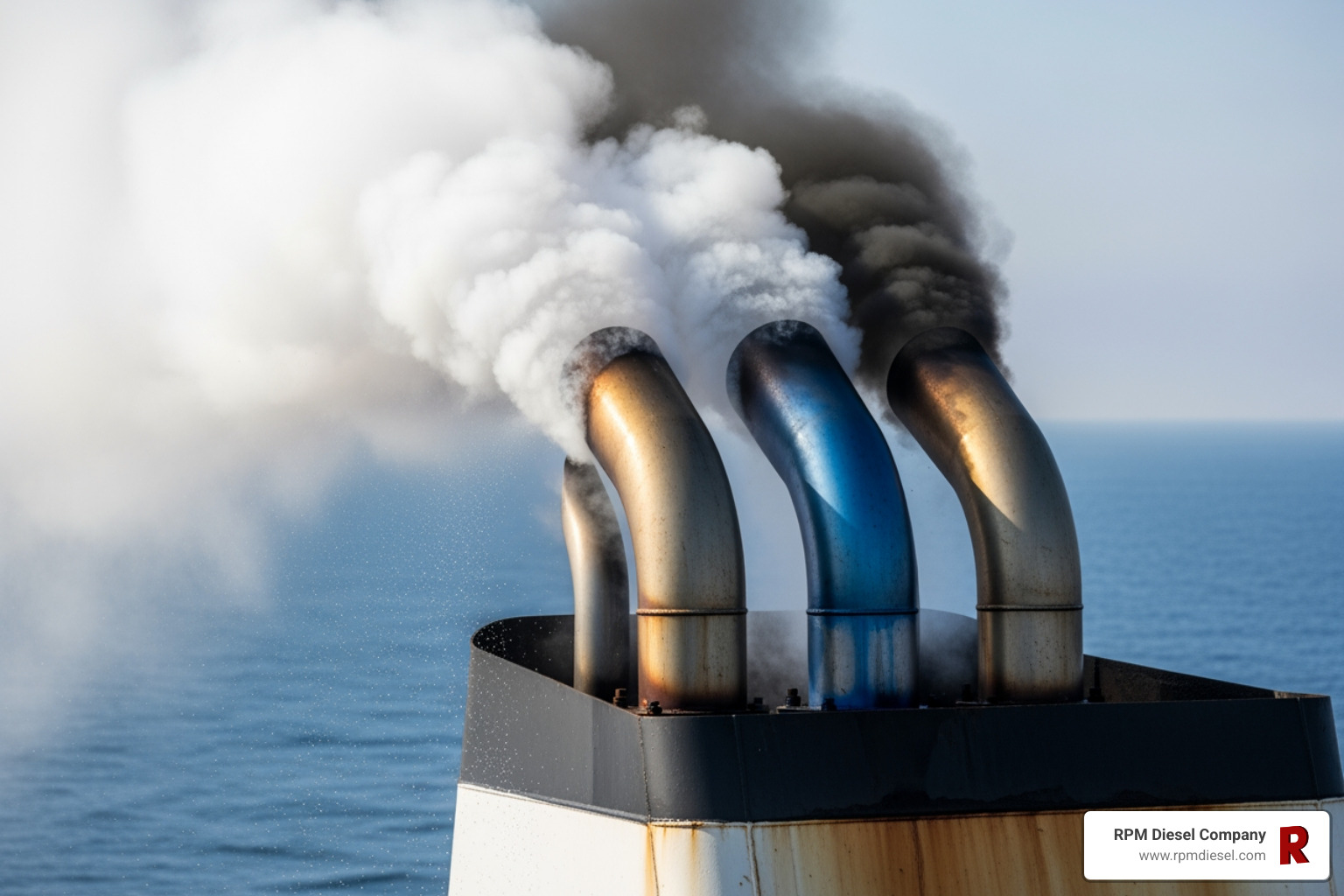

- Black Smoke: Indicates too much fuel or not enough air. Causes include overloading, a dirty air filter, or faulty injectors/injection pump.
- Blue Smoke: Indicates burning oil. Causes include worn piston rings or valve seals. Often has a distinct burning oil smell.
- White Smoke: Points to water, coolant, or unburnt fuel. Causes include a blown head gasket, incorrect injection timing, or bad fuel. A sweet smell indicates coolant; a fuel smell indicates unburnt diesel.
Engine Overheating in a Marine Environment
Overheating is a critical issue for marine diesels. In Florida’s warm waters, it’s a common threat.
- Raw Water Cooling System Issues:
- Clogged Sea Strainer: A clogged sea strainer is a top cause of overheating. Check it for debris like seaweed or plastic.
- Impeller Failure: The raw water pump’s rubber impeller can fail, stopping water circulation. Inspect it regularly.
- Blocked Raw Water Intake: Marine growth can block the raw water intake thru-hull.
- Heat Exchanger Blockage: Internal salt deposits or corrosion can clog the heat exchanger, reducing cooling efficiency.
- Thermostat Issues: A thermostat stuck in the closed position will cause rapid overheating.
- Low Coolant Level: A coolant leak will reduce the system’s ability to cool the engine. Check levels when the engine is cool.
Advanced Diagnostics and Fault Codes
Modern Kubota diesel engines often have Electronic Control Units (ECUs) that generate fault codes, which are invaluable for troubleshooting. These codes can trigger “limp mode,” reducing engine power to prevent damage.
Understanding Common Kubota Diesel Engine Fault Codes
Here’s a table of some common Kubota diesel engine fault codes and their typical meanings:
| Fault Code | Description | Common Causes & Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| P3001 | Emissions Deterioration (DPF) | High soot in DPF. Requires forced regeneration. Regular DPF maintenance is key. |
| P0087 | Low Fuel Rail/System Pressure | Caused by a clogged fuel filter, faulty pump, sensor, or damaged lines. Check the fuel delivery path. |
| P0563 | Battery Voltage Abnormality (High) | Indicates overcharging, often from a faulty alternator regulator. Test charging system and wiring. |
| P2293 | Abnormal Fuel Pressure Regulator Performance | Fuel pressure regulator is failing to maintain correct pressure, causing poor performance. Inspect or replace the regulator. |
| P2294 | Fuel Pressure Regulator Malfunction (Circuit) | Caused by wiring issues or a bad fuel pressure regulator. Check wiring for corrosion; if good, replace the regulator. |
| P3008 | Cam Position Sensor Circuit Fault | Faulty camshaft position sensor or wiring. This sensor is critical for timing. Check wiring/connectors, then test/replace sensor. |
Always consult your specific Kubota engine’s service manual for the most accurate interpretation of fault codes.
Advanced Kubota Diesel Engine Troubleshooting Tests
Some issues require more in-depth tests.
- Injector Contribution Test: What is a contribution test for injectors, and how is it performed? This test helps identify a weak or faulty fuel injector.
- Traditional Method (Mechanical): On a running engine, carefully loosen the fuel line at one injector at a time. A good injector will cause an RPM drop. No change indicates a faulty injector. Caution: High-pressure fuel is dangerous.
- Modern Method (Electronic): On electronic engines, a diagnostic tool can perform a “cylinder cutout test” to identify faulty injectors safely.
- Injection Pump Diagnosis: How can we diagnose issues with the injection pump on a Kubota diesel engine? Diagnosing an injection pump is complex and often requires a professional. Basic checks include testing fuel pressure, volume, and timing.
- Vibration Analysis: Vibration analysis is a powerful diagnostic tool for internal engine issues. Specialized equipment measures engine vibrations, and experts analyze the patterns to pinpoint problems like misfires, piston slap, or fuel injection faults. This is particularly crucial for managing marine vessels (overview: Diesel engine vibration analysis).
How to Reset Kubota Engine Fault Codes
Resetting codes varies by model.
- Manual Reset Procedures: Some models have manual reset procedures involving specific key turns or button presses. Always consult your service manual for the correct procedure for your engine.
- Using a Diagnostic Tool: For modern engines, a diagnostic scan tool is the best way to read and clear codes. Only clear codes after fixing the underlying issue, or they will return.
Frequently Asked Questions about Kubota Marine Diesel Engines
What are the most common reasons a Kubota marine diesel engine won’t start?
The most common issues are related to the fuel and electrical systems. This includes dead or weak batteries, corroded connections, clogged fuel filters, air in the fuel lines, or poor-quality fuel.
What do different colors of exhaust smoke mean on my Kubota engine?
Black smoke typically indicates incomplete combustion, often from a clogged air filter or an overloaded engine. Blue smoke means the engine is burning oil, likely due to worn piston rings or valve seals. White smoke often points to water or coolant entering the combustion chamber or incorrect injection timing.
What should I do if I suspect water has contaminated my diesel fuel?
Water contamination, especially in a marine environment, is serious. You should immediately stop the engine if possible. The fuel tank will need to be drained and cleaned, fuel filters replaced, and the entire fuel system purged of water and bled to remove air.
The Best Fix is Prevention: Your Maintenance Checklist
Preventive maintenance is the best way to ensure your Kubota marine diesel’s reliability and longevity, especially in Florida’s harsh marine environment.
Crucial Maintenance Schedule
Adhering to a strict maintenance schedule is essential.
- Daily Checks (Before each trip):
- Check oil, coolant, and fuel levels.
- Inspect for leaks.
- Check the raw water strainer for debris.
- Every 50-250 Hours (or Annually):
- Engine Oil and Filter Change: Change engine oil and filter per your manual’s interval, using the recommended oil for Florida’s climate.
- Fuel Filter Replacement: Replace primary and secondary fuel filters to prevent fuel system problems.
- Air Filter Inspection/Cleaning: Inspect, clean, or replace the air filter element.
- Battery Maintenance: Clean battery terminals, check connections, and test charge.
- Fan Belt Inspection: Inspect fan belt for tension and wear.
- Hose and Clamp Inspection: Inspect all hoses and clamps for cracks or leaks; replace as needed.
- Every 500-1000 Hours (or Bi-Annually):
- Cooling System Service: Service the cooling system: flush coolant, inspect/replace the raw water pump impeller, and consider replacing raw water hoses.
- Valve Clearance Check: Have a technician check and adjust valve clearance.
- Fuel Injection System Inspection: Have injectors professionally inspected.
- Every 1500+ Hours (or as needed):
- Injection Pump Check: Have the injection pump checked for calibration and timing.
- Turbocharger Inspection: If equipped, inspect the turbocharger.
Disciplined maintenance saves time and money on future repairs.
When to Call a Professional
While many troubleshooting steps can be done by a knowledgeable owner, some situations require an expert. When should you seek professional help for Kubota diesel engine troubleshooting?
- Complex Internal Engine Work: Internal engine work (pistons, valves, crankshafts) requires specialized tools and expertise.
- Injection Pump Service: Injection pump service is highly specialized and should be left to certified professionals.
- ECU and Advanced Electronic Diagnostics: Troubleshooting ECUs and complex electronic faults requires advanced training.
- Persistent Problems: If you can’t solve a persistent problem, call an expert to avoid more costly damage.
- Safety Concerns: For any repair you’re unsure about, especially with fuel or electrical systems, consult a professional for safety.
For reliable marine diesel engine repair in Fort Lauderdale, Miami, and across South Florida, the RPM Diesel Company team is here to help. We specialize in Kubota engines and can get your vessel running smoothly. Don’t let a complex problem keep you stalled; contact us for professional diesel engine repair.